
-
Courses
-
Domains
- CAD/CAM
- AI/Machine Learning
- Piping
- MS Dynamics®
- Cloud Computing
- Big Data
- Civil Design
- Service Management
- Robotics
- Data & Analytics
- Mechanical CAD
- Database
- Embedded System
- Software Quality Testing
- Data Science
- Information Security
- Prog. & Development
- Virtualization
- Project Management
- Mobile Web Development
- Salesforce
- Brands
- Training
-
Domains
-
Courses
- Project Management
- Data and Analytics
- Data Visualization
- Hadoop
- SAS®
- MS Excel
- R Programming
- Learning Data Analysis with R
- Fundamentals of R Programming and Statistical Analysis
- Learning Python Data Analysis
- CBAP®
- Kibana: Essentials
- Mastering Wireshark 2
- Advanced Data Mining projects with R
- R Data Mining Projects
- Fast Data Processing Systems with SMACK stack
- Data Warehousing
- Talend Certification Training Online
- Data Science
- Robotics
- Big Data
- Apache Storm
- Apache Spark
- Apache Kafka
- Data Science with Spark
- Impala
- Splunk Developer & Admin
- Comprehensive Hive
- Comprehensive Pig
- Mastering Apache Ambari
- Hadoop Admin
- Hadoop Dev (Hadoop)
- Hadoop Data Analytics
- Apache Spark and Scala
- Apache Hbase Online Training
- Big Data Hadoop Architect Online Training
- Big Data Analyst Online Training
- Business Intelligence
- Actuate Birt
- AbInitio
- Oracle® Database
- MicroStrategy
- Microsoft®
- MCSA: SQL Server 2016 Business Intelligence Development
- 10989 Analyzing Data With Power BI
- MCSE BI 2012
- Implementing Data Models and
Reports with MS SQL Server 2012
(70-466) - Designing BI Solutions with MS
SQL Server 2012 (70-467) - MSCE BI 2008
- Microsoft® SQL Server™ 2008
Analysis Services - Microsoft® SQL Server™ 2008
Integration Services - Microsoft® SQL Server™ 2008
Reporting Services - Analyzing and Visualizing Data with Power BI
- Business Intelligence in MS Dynamics CRM 2016
- Process Modeling Using BPMN
- Pentaho
- Spotfire
- Qlik Sense Online Certification
- Tableau 10 BI Solutions - Volume 2
- Cloud Computing
- AWS
- Microsoft®
- AZ-500: Microsoft Azure Security Technologies
- AZ-301: Microsoft Azure Architect Design
- AZ-300: Microsoft Azure Solutions Architect Technologies
- AZ-104: Microsoft Azure Administrator
- Windows® Store Apps using C#
- Developing Microsoft® Azure Solutions
- Managing Office 365 Identities and Services
- Implementing MS Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- 20247: Configuring and Deploying a Private Cloud
- Infrastructure as a Service Solutions with Azure
- Azure Platform as a Service - Web and API Application Deployment
- 40577-G: Microsoft Cloud Workshop: Innovate and modernize apps with Data and AI Online Training
- AZ-304: Microsoft Azure Architect Design Online Training
- AZ-204: Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure Certification Online Training
- AZ-204: Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure Certification Online Training in Dubai
- AZ-220T00: Microsoft Azure IoT Developer Online Training
- AZ-020T00-A: Microsoft Azure solutions for AWS developers Online Training
- AZ-120T00: Planning and Administering Microsoft Azure for SAP Workloads Online Training
- SC-300T00: Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator Online Training
- Microsoft AZ 600t00 Online Training
- AZ-400 Designing and Implementing DevOps Solutions Online Training
- DP-203T00: Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Online Training
- Oracle
- Salesforce®
- Google®
- Cloud Computing
- Blockchain Certification Training
- Blockchain Ethereum Developer
- Kubernetes
- OpenStack
- DevOps Online Training
- Chef DevOps
- ServiceNow Admin
- Learning Salt
- Servicenow Customer Service Management Fundamentals Online Training
- Saviynt Online Training
- Snowflake Online Training
- Kubernetes Administration Using Docker Online Training
- SailPoint: File Access Manager Implementation and Administration: Essentials v8.1 Online Training
- Identity
- Microsoft®
- Cloud Computing
- AZ-500: Microsoft Azure Security Technologies
- AZ-303: Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies Online Training
- AZ-301: Microsoft Azure Architect Design
- AZ-300: Microsoft Azure Solutions Architect Technologies
- AZ-104: Microsoft Azure Administrator
- MCSA: Cloud Platform
- Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
- Windows® Store Apps using C#
- Developing Microsoft® Azure Solutions
- Managing Office 365 Identities and Services
- Implementing MS Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- 20247: Configuring and Deploying a Private Cloud
- AZ-204: Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure Certification Online Training
- 40577-G: Microsoft Cloud Workshop: Innovate and modernize apps with Data and AI Online Training
- AZ-303: Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies Online Training
- AZ-304: Microsoft Azure Architect Design Online Training
- AZ-204: Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure Certification Online Training
- AZ-204: Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure Certification Online Training in Dubai
- AZ-220T00: Microsoft Azure IoT Developer Online Training
- AZ-020T00-A: Microsoft Azure solutions for AWS developers Online Training
- AZ-120T00: Planning and Administering Microsoft Azure for SAP Workloads Online Training
- SC-300T00: Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator Online Training
- Microsoft AZ 600t00 Online Training
- AZ-400 Designing and Implementing DevOps Solutions Online Training
- DP-203T00: Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Online Training
- Database
- 20761A: Querying Data with Transact-SQL 2016
- (SSRS) Analyzing Data with SQL Server 2016 Reporting Services
- (SSIS) Implementing SQL 2016 Data Warehouse
- (SSAS) Developing SQL 2016 Data Models
- MCSA SQL Server 2012
- MCSE BI 2012
- Implementing Data Models and
Reports with MS SQL Server 2012
(MS-SQL 2012) - Designing BI Solutions with MS
SQL Server 2012 (70-467) - Microsoft® SQL Server BI 2008
- Microsoft® SQL Server™ 2008
Analysis Services - Microsoft® SQL Server™ 2008
Integration Services - Microsoft® SQL Server™ 2008
Reporting Services - 10989 Analyzing Data With Power BI
- SQL Server 2012 High Availability
- 10774 Querying Microsoft SQL Server 2012
- 10777 Implementing A Data Warehouse With Microsoft SQL Server 2012
- 20461: Querying Microsoft SQL Server 2014 Databases
- 10961: Automating Administration with Windows PowerShell
- 20764: Administering a SQL Database Infrastructure (SQL Server 2016)
- DP-300T00-A: Administering Relational Databases on Microsoft Azure Online Training
- Server
- 20740B: Installation Storage & Compute With Windows Server 2016
- 20741B: Networking With Windows Server 2016
- 20742B: Identity With Windows Server 2016
- 20743B: Upgrading MCSA: Windows Server 2016
- 20773A- Analyzing Big Data with Microsoft R
- 20774A- Perform Cloud Data Science with Azure Machine Learning
- 20775A - Performing Data Engineering on Microsoft HDInsight
- MCSA: SQL Server 2016 Business Intelligence Development
- MCSA: SQL Server 2016 Database Development
- MCSA® 70-410
- MCSA® 70-411
- MCSA® 70-412
- Developing Microsoft SharePoint Server 2016 Solutions
- MCSA®: Windows Server 2016
- Microsoft®: 70-744: Securing Windows Server 2016
- MCSA®: Windows Server 2012
- MCSA®: Windows Server 2012
- SharePoint 2016 Power User
- MCSD SharePoint® Server 2013 Dev
- MCSE SharePoint® Server 2013 Administrator
- Advanced Automated Administration with Windows PowerShell®
- BizTalk Server 2016 Developer
- BizTalk Server 2016 Administration
- BizTalk Server 2006
- Microsoft Lync Server
- MS Team Foundation Server 2010
- Windows 10 MCSA
- 55286-A: SharePoint 2019 Power User Online Training
- Exchange Server
- System Center
- MS Configuration Manager (SCCM 2012)
- Advanced Microsoft SCCM Current Branch Scenarios
- MS Admin System Center Config Manager
- System Center 2012 Orchestrator
- Cloud & Datacenter Monitoring
- Getting Started with System Center 2016 Operations Manager
- Course 55164-A: Quick Powerful Graphics with Power View, PowerPivot, Power Query, Power Map and Power BI Online Training
- Applications
- Mastering Microsoft Project 2016
- Skype for Business
- Managing Office 365 Identities and Services
- Enabling and Managing Office 365
- IIS7
- MS Excel
- MS Advance Excel
- Advanced Microsoft Excel 2016
- PL-900T00-A: Microsoft Power Platform Fundamentals Online Training
- DP-090T00: Implementing a Machine Learning Solution with Microsoft Azure Databricks Online Training
- 55278-A: Advanced Microsoft Outlook 2019 Certification Online Training
- 55289-A: Microsoft Project 2019: Digging Deeper Online Training
- Cloud Computing
- Oracle®
- Database
- SOA Suite 12c: Build Composite Applications
- 12c: New Features Admin
- 12c: SQL Tuning for Developers Ed1
- 12c admin install and upgrade accelerated
- Oracle 12c DBA
- Oracle SOA Suite 12c
- 12c: RAC Administration
- Introduction to SQL
- 11g: RAC and Grid Infrastructure Admin Accelerated 2
- 11g: Administration Workshop I
- 11g: Administration Workshop II
- 11g: Database Administration OCA
- PL/SQL
- Essbase 11.1.2 for System
Administrators - MySQL Performance Tuning Ed 3
- 11g RAC Administration R 2
- Oracle Access Manager 11g R2: Admin
- Identity Manager 11g R2: Essentials
- Oracle Weblogic Server
- Web Services foundation Using xml for Framework 4 ED 1
- Web Services Advanced Using XML for Framework 4 ED 2
- R12.x Oracle Inventory Management Fundamentals
- Oracle Database 12c: Data Guard Administration Course Online (1Z1-066)
- Oracle® PeopleSoft
- Oracle® EBS
- Oracle® Hyperion
- Business Intelligence
- GoldenGate
- Cloud
- Database
- CAD/CAM
- Civil
- AVEVA E3D (Everything 3D) Admin Online Training
- AutoCAD® 2D & 3D
- STAAD.Pro® v8i
- Revit® Structure
- Autodesk Robot Structural Analysis Online Training
- Autodesk® BIM 360™
- Navisworks
- ETABS
- AutoCAD Civil 3D Grading
- AutoCAD® P&ID
- Structural Analysis Computer System
- RISA Foundation
- MaxSurf Online Training
- Road Design & Analysis using MXROAD
- Bentley OpenRoads Designer Online Training
- Mechanical
- Hypermesh
- Magma5
- CATIA®
- CATIA® V6 2013x - 103 Assembly Design
- CATIA® V6 2013x - 201 Drafting
- CATIA® V6 2013x - 100 Essentials for New Users
- CATIA® V6 R2015x Essentials for Users
- CATIA® V6 R2016x Essentials for Users
- SolidWorks®
- SOLIDWORKS API Fundamentals
- UG-NX
- Delcam
- Revit® MEP
- Inventor
- ANSYS Fluent Online Training
- ANSYS
- Introduction to Abaqus
- NX 2 Automotive Interior Trim
- Architecture
- Electrical
- Piping
- AutoCAD Piping
- AutoCAD P&ID Essential Online Training
- Piping Design & Drafting
- Intergraph CAESAR II®
- SP3D®
- SP3D Admin
- SP3D Civil
- SP3D Electrical
- PDMS
- PDMS Administration
- SPI/INtools
- Air Conditioning System Design (HVAC)
- Process Instrumentation & Control
- SM3D
- SmartPlant P&ID
- SmartPlant® 3D (SP3D) Online Training Course
- Others
- Civil
- Oracle® ERP
- Dynamics®
- NAV 2018
- NAV 2017
- NAV 2015
- NAV 2013
- AX 2012
- AX 2012 Development
- Development I AX 2012 R3
- Development II AX 2012 R3
- AX Financials
- Financial I AX 2012 R3
- Financial II AX 2012 R3
- Project Management and Accounting - Basic AX 2012 R3
- Data Management AX 2012 R3
- Bill of Materials AX 2012 R3
- Supply Chain Foundation AX 2012 R3
- Transportation Management AX 2012 R3
- Distribution and Trade in MS Dynamics AX 2012 R3
- Fixed Assets in MS Dynamics AX 2012 R3
- Reporting in AX 2012 R3
- AX Distribution and Trade
- AX 2012 R3 Installation and Configuration
- AX 2012 R3 Retail Application
- AX 2012 R3 HR and Payroll
- AX 7 Finance
- 80694AE: Warehouse Management
- 80696AE: SQL Optimization
- 80716AE: Retail Channel Management and Corporate Operations
- Dynamics 365
- CRM 2016
- CRM 2013
- Oracle® PeopleSoft
- Oracle® EBS
- Oracle® Hyperion
- Dynamics®
- Internet of Things
- Virtual Reality
- Embedded Systems
- Service Management (ITIL)
- Digital Marketing
- Virtualization
- CompTIA
- Database
- MongoDB Admin
- MongoDB Developer & Admin
- Cassandra
- Microsoft
- 20761A: Querying Data with Transact-SQL 2016
- (SSRS) Analyzing Data with SQL Server 2016 Reporting Services
- (SSIS) Implementing SQL 2016 Data Warehouse
- (SSAS) Developing SQL 2016 Data Models
- MCSA SQL Server 2012
- MCSE BI 2012
- Implementing Data Models and
Reports with MS-SQL Server 2012
(MS-SQL 2012) - Designing BI Solutions with MS
SQL Server 2012 (70-467) - Microsoft® SQL Server BI 2008
- Microsoft® SQL Server™ 2008
Analysis Services - Microsoft® SQL Server™ 2008
Integration Services - Microsoft® SQL Server™ 2008
Reporting Services - 10989 Analyzing Data With Power BI
- SQL Server 2012 High Availability
- 10774 Querying Microsoft SQL Server 2012
- 10777 Implementing A Data Warehouse With Microsoft SQL Server 2012
- 20461: Querying Microsoft SQL Server 2014 Databases
- 10961: Automating Administration with Windows PowerShell
- Oracle
- SOA Suite 12c: Build Composite Applications
- 12c: New Features Admin
- 12c: SQL Tuning for Developers Ed1
- 12c admin install and upgrade accelerated
- Oracle 12c DBA
- Oracle SOA Suite 12c
- 12c: RAC Administration
- Introduction to SQL
- 11g: RAC and Grid Infrastructure Admin Accelerated 2
- 11g: Administration Workshop I
- 11g: Administration Workshop II
- 11g: Database Administration OCA
- PL/SQL
- Essbase 11.1.2 for System
Administrators - MySQL Performance Tuning Ed 3
- 11g RAC Administration R 2
- Oracle Access Manager 11g R2: Admin
- Identity Manager 11g R2: Essentials
- Oracle Weblogic Server
- Web Services foundation Using xml for Framework 4 ED 1
- Web Services Advanced Using XML for Framework 4 ED 2
- Jenkins
- NoSQL Database
- MEMSQL 6.5 ADMINISTRATOR
- Neo4J
- MariaDB for Developers
- MariaDB Administration
- Apache CouchDB for Developers
- PostgreSQL Administration & Development
- Redis
- Apple/iOS®
- Programming & Development
- Programming
- Web Development
- Progressive Web Application Development
- Core Java®
- Oracle JAVA SE 8
- ReactJS with Redux
- React Redux React-Router
- MuleSoft.U Development Fundamentals (Mule 3)
- Node.js
- Vue.js
- Introduction to TypeScript
- React Native
- Oracle JAVA Advanced Framework
- Core PHP
- PHP 7 Programming Solutions
- HTML5 & CSS3
- PERL Scripting
- Developing ASP.NET MVC 4 Web Applications
- Windows® Apps using C#
- Full Stack Web Developer
- Mastering Go Programming
- Getting Started with PHP 7
- Adobe Flex
- Laravel PHP Framework
- Web Development with Angular 2 and Bootstrap
- Mastering Node.js
- Getting Started with Unity 2D Game Development
- Drupal 8 for Beginner
- Angular 2 Solutions - Advanced Concepts
- Mastering Bootstrap 4
- Test-Driven Android
- Visual Studio 2015 Solutions - Part 1
- Mobile/Web Development
- iPhone®
- Android®
- Create Android apps with App Inventor
- Windows® Apps using C#
- HTML5 & CSS3
- Ruby On Rails
- Angular 7
- Angular 6
- Angular 4
- Angular2
- Angular 2 Web Development with TypeScript
- Angular JS
- jQuery
- XAMARIAN
- Ionic Framework
- Mobile Ui Design Essentials
- NativeScript
- PhoneGap
- Backbone.js
- MEAN Stack Development
- Django
- Python, MySQL and Django
- Android App development with Kotlin Online Training
- Angular 11 Online Training
- MCSD SharePoint® Server 2013 Dev
- MCSE SharePoint® Server 2013 Admin
- Macro and VBA Excel
- Docker
- Akka With Scala
- Software Quality Testing
- Cisco®
- Red Hat®
- Information Security
- EC-Council
- CheckPoint
- Linux
- IBM®
- Security QRadar SIEM 7.2 Admini
and Config - IBM® Certified Solution Designer - WebSphere® MQ V7 Online Certification Training
- IBM® Websphere® Transformation Extender - Essentials Online Certification Training
- IBM® Certified System Administrator- Websphere Application Server Network Deployment V8.5 and Liberty Profile Online Training
- IBM® Certified Solution Developer - WebSphere Message Broker V7 Online Certification Training
- IBM® Cognos BI Administration Online Certification Training
- IBM® InfoSphere DataStage Essentials Online Certification Training
- DB2 for Linux, UNIX, and Windows Performance Tuning and Monitoring Workshop ILT Online Certification Training (CL412G)
- IBM® AIX Basics ILT Online Certification Training (AN10G)
- IBM® Cognos ICM - Building Reports V9 Online Certification Training (1R119G)
- IBM® FileNet P8 Platform 5.2 - Installation ILT Online Certification Training (F211G)
- IBM® Tivoli Storage Manager 6.3 Implementation and Administration ILT Online Training (TS612G)
- IBM® Integration Bus V9 Application Development I ILT Online Certification Training (WM665G)
- IBM® WebSphere Application Server V8 Administration for Windows Online Certification Training (WA380G)
- IBM InfoSphere MDM Architecture V11 ILT Online Certification Training (ZZ820G)
- IBM® Tivoli Netcool Impact 7.1 Administration and Implementation ILT Certification Training (TN045G)
- IBM® Understanding Business Process Manager ILT Online Training (VW901G)
- IBM® Security QRadar SIEM Foundations ILT Online Certification Training (BQ102G)
- IBM® Introduction to Bluemix ILT Online Certification Training
- IBM® Tivoli Monitoring 6.3 for Implementers ILT Online Certification Training (TV355G)
- IBM FileNet Content Manager 5.2 - Implementation and Administration ILT Online Certification Training (F115G)
- IBM® Lotus Domino 8.5 System Administration Fundamentals ILT Online Training (D8L75G)
- IBM® Netcool OMNIbus 8.1 Administration and Maintenance ILT Online Training (TN035G)
- IBM® Security Identity Manager 6.0 Basic Administration ILT Online Training (TW253G)
- IBM® Sterling Selling and Fulfillment Suite Participant Modeling and User Security ILT Online Certification Training (6F02G)
- Security QRadar SIEM 7.2 Admini
- Palo Alto Next Generation Firewall Administration
- Web Application Security
- COBIT®5
- JIRA-Bug Tracking And Project Management Tool
- MS Dynamics®
- NAV 2018
- NAV 2017
- NAV 2016
- NAV 2015
- NAV 2013
- AX 2012
- AX 2012 Development
- Development I AX 2012 R3
- Development II AX 2012 R3
- AX Financials
- Financial I AX 2012 R3
- Financial II AX 2012 R3
- Project Management and Accounting - Basic AX 2012 R3
- Data Management AX 2012 R3
- Bill of Materials AX 2012 R3
- Supply Chain Foundation AX 2012 R3
- Transportation Management AX 2012 R3
- Distribution and Trade in MS Dynamics AX 2012 R3
- Fixed Assets in MS Dynamics AX 2012 R3
- Reporting in AX 2012 R3
- AX Distribution and Trade
- AX 2012 R3 Installation and Configuration
- AX 2012 R3 Retail Application
- AX 2012 R3 HR and Payroll
- AX 7 Finance
- 80694AE: Warehouse Management
- 80696AE: SQL Optimization
- 80716AE: Retail Channel Management and Corporate Operations
- Microsoft Dynamics 365
- Introduction
- Agent Enablement
- Customizations & Configurations
- Sales Management
- 81055AE: Relationship Management
- 81067AE: Development Environment Intro
- Customer Engagement Core Associate
- Customer Service Functional Consultant Associate
- Customer Engagement for Customer Service Associate
- Field Service Associate
- MB-900T01: Dynamics 365 Fundamentals
- Customer Service Functional Consultant Associate
- Sales Functional Consultant Associate
- MS-100T00-A: Microsoft 365 Identity and Services
- MB-200: Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Engagement Core Associate
- Microsoft Certified Dynamics 365 for Customer Service Functional Consultant Associate Certification Online Training Course
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Retail Online Training
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Talent Online Training
- Get started with Dynamics 365 Commerce Online Training
- MB-220T00: Microsoft Dynamics 365 Marketing Online Training
- CRM 2016
- CRM 2013
- MB-330T00-A: Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management Online Training
- SAP®
- SAP® BASIS
- SAP® PM
- SAP® ABAP
- SAP® CO
- SAP® (SAP-FI/CO)
- SAP® HR
- SAP® SD
- SAP® MM
- SAP® Quality Management
- SAP® CRM Functional
- SAP® HANA
- SAP® BI
- SAP® BO
- BOE310 - SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence Platform: Administration and Security Online Training
- SAP® EHS
- SAP® Success Factors
- SAP® Warehouse Management
- SAP® NetWeaver
- SAP C4C Technical
- SAP FIORI
- SAP Hybris (DEV & FUN)
- SAP Hybris Cloud for Customer - Project Implementation
- SAP Hybris Cloud for Sales
- SAP Hybris Cloud for Service
- SAP UI5
- SAP APO
- SAP BODS
- SAP Arib
- SAP Leonardo Machine Learning Foundation
- SAP PI/PO 7.4
- SAP S/4HANA Finance 1809
- SAP S/4HANA Logistics 1809
- SAP SCM
- SAP Security
- SAP SuccessFactors Onboarding and Recruiting
- C4H340 - SAP Commerce Cloud Developer Part 1 Course Online Training
- C4H341 - SAP Commerce Cloud Developer Part 2 Course Online Training
- SAP BPC
- SAP HANA Cloud Integration
- SAP IS Oil & Gas
- SAP IS Retail
- SAP IS Utilities
- PS Business Processes in SAP Project Management
- PS Master Data Configuration in SAP Project System
- PS Project Management – Controlling
- PS Project Management - Logistics
- SAP IBP
- SAP BW 7.5 on HANA
- SAP S/4 HANA Finance 1909
- CLD900 - SAP Cloud Platform Integration Online Training
- HR940 - Authorizations in SAP HR Online Training
- HR862-SAP SuccessFactors Learning Management Administration Online Training
- HR800 SAP SuccessFactors Platform Administration Online Training
- HR505 - Organizational Management Online Training
- HR580 - Analytics and Reporting in HCM Online Training
- HR305 - Configuration of Master Data Online
- HR306 - Configuration of Time Recording Online Training
- SAP Analytics Cloud Training
- Business Processes in SAP Project Systems Online Training
- SAP S/4HANA Logistics 1909 Training Online
- E2E600 Implementation Projects with SAP Solution Manager 7.2 Online Training
- BOD410-SAP Lumira Designer Basic Online Training
- SAP Marketing Cloud Online Training
- SAP® - Financial / Controlling (SAP - FI/CO) Online Certification Training
- CLD900 - SAP Integration Suite Online Training
- CP100 - SAP Cloud Platform Online Training
- ADM540 - Database Administration SAP ASE for SAP Business Suite Online Training
- Training
- Resource
- Training
- Resources
-
Log in
- All Domain
-
Microsoft
- Microsoft Power Platform Solution Architect (PL-600)
- Microsoft Power Platform App Maker Training (PL-100)
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Retail Training
- Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst ( PL- 300 )
- Microsoft 365 Mobility And Security (MS-101)
- Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals ( DP-900 )
- Administering A SQL Database Infrastructure
- Microsoft Azure DevOps ( AZ-400 )
- MB-220: Microsoft Dynamics 365 Marketing Training
- Microsoft Azure Architect Design (AZ-304 )
- Microsoft Azure Security Technologies ( AZ-500 )
- Microsoft Azure Pricing and Billing Training
- Data Engineering On Microsoft Azure (DP-203)
- Microsoft Azure Solutions Architect Training
- MS Dynamics 365 Finance Training
- PL- 300 Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst Training
- Microsoft Azure Active Directory Training
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Technical Training
-
Cloud Computing
- Salesforce Financial Services Cloud (FSC) Training
- Kronos UKG Training
- ServiceNow Training
- Salesforce App Builder (DEV 401) Training
- ServiceNow IT Asset Management (ITAM) Training
- SalesForce Sales Cloud Consultant Training
- SailPoint Training
- Sailpoint IdentityNow Training
- SailPoint IdentityIQ Training
- PingDirectory Admin Training
- Salesforce Billing Training
- Servicenow Customer Service Management Fundamentals Training
- Snowflake Training
- Saviynt Training
- Workday Advanced Reporting Training
-
Big Data
- Apache Spark with Scala Course
- Data Science Online Training
- Data Scientist with R Course
- Hadoop Developer Course
- Hadoop Administration Online Training
- Apache Hbase Course
- Hadoop Data Analytics Online Training
- Splunk Administration Online Training
- Machine Learning with MATLAB Training
- TensorFlow Online Training
- Hands-On Python & R In Data Science Course
- Deep Learning A-Z Hands-On Artificial Neural Networks Training
- AI & Deep Learning with TensorFlow Course
- Splunk Operational Intelligence Training
- Artificial Intelligence Online Training
- Support Vector Machines Course
- General Boosting & Bagging Course
- Introduction to Machine Learning Course
-
Agile Scrum
- Certified Scrum Developer® (CSD) Training
- Certified Agile Leader Training
- Agile Automation Testing Training (ICP-ATA Certification) Course
- Professional Scrum Product Owner (PSPO) Training
- SAFe® 6.0 POPM Training
- SAFe 6.0 Release Train Engineer (RTE) Training
- Agile Scrum Master (ASM) Training
- Certified Scrum Product Owner CSPO Training
- PeopleCert SCRUM Master I Training
- SAFe 5 Agilist Training
- SAFe 5 POPM Training
-
Data Analytics
- Data Science
- Advance Excel
- Dayforce Training
- Tableau Training
- Informatica Data Engineering Training
- Advance SAS
- R Programming
- Python Training
- Data Science With Python
- Data Science With R
- Data Science, Python, R & Machine Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Qlik Sense Certification
- SPLUNK DEVELOPER & ADMIN
- ELK: Elasticsearch, Logstash And Kibana For Administrators
- Kibana: Essentials Training
- Python, MySQL And Django Online Training
-
Piping
- SmartPlant 3D (SP3D)
- SP3D Civil
- Aveva Diagrams
- AVEVA E3D Equipment Online Training
- AVEVA E3D Piping Online Training
- Piping Design & Engineering With PDMS Training
- Process Engineering Online Training
- Aveva Diagrams (User) Online Training
- AutoCAD P&ID Essential Online Training
- AVEVA E3D (Everything 3D) Admin Online Training
- SmartPlant P&ID Online Training
- SmartPlant P & ID Admin
- AutoCAD® 2D And 3D Training
- PDMS Training
- SmartPlant Instrumentation (SPI) Intools
- Process Instrumentation And Control
- Intergraph CAESAR II Training
-
AWS
- AWS Data Engineering Training
- AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials Training
- AWS Solution Architect - Professional Level Training
- AWS Solution Architect - Associate Level Training
- AWS SysOps Engineering Training
- AWS Certified Developer Associate Training
- AWS Certified Sysops Admin (SOA-C02) Training
- AWS Cloud Computing Concepts Training
- AWS Certified Big Data Specialty Training
- AWS Certified Data Analytics Specialty Training
- AZ-030 Microsoft Azure Technologies for AWS Architects Training
- AWS Certified Security Engineering Online Training
- Migrating Applications to AWS Training
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Training
- AWS DevOps Engineer Training Course
-
CAD/CAM
- Aveva Diagrams Course
- Bentley OpenRoads Designer Training
- PLC Automation Course
- AutoCAD P&ID Essential Course
- ANSYS Fluent Course
- Autodesk Robot Structural Analysis Training
- AVEVA E3D Admin Online Training
- SmartPlant Spoolgen Training
- SmartPlant P&ID Training Course
- Rhino Intermediate & Advanced Training
- CANoe Online Training
- Simultaneous Monocular Mapping and 3D (SM3D) Training Course
- 3D Printing Course
- SPEL Admin Training
- SmartPlant Instrumentation/INtools (SPI) Training
- Road Design & Analysis using MXROAD Training
- Electrical Instrumentation Design Course
- AutoCAD P&ID Course
- AutoCAD Electrical Online Training
- MaxSurf Online Training
-
Database
- OpenEdge Database Administration Training
- Oracle Database Online Certification Training
- MCSE Business Intelligence Online Training
- Linux Device Driver Training
- PLC Automation Training
- Microsoft SQL Server Databases Training Course
- 20740B: Installation Storage and Compute With Windows Server 2016
- MEMSQL Admin Training Certification Course Online
- Jenkins Online Certification Training
- Neo4J & Certification Course
- NoSQL Database
- Apache CouchDB for Developers Course
- MariaDB Administration
- MariaDB for Developers
- PostgreSQL Administration & Development
- Redis
- Oracle Database 12c: SQL Tuning for Developers Ed1
-
MS Dynamics
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016 Trade & Logistics Course
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016 Core Setup and Finance Course
- Exploring Microsoft Dynamics NAV Course
- Installing and Configuring Microsoft Dynamics NAV Course
- Fixed Assets in Microsoft Dynamics NAV Course
- Finance Essentials in Microsoft Dynamics NAV Course
- Finance Advanced in Microsoft Dynamics NAV Course
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV Course
- Application Setup in Microsoft Dynamics NAV Course
- Development Environment Intro in MS Dynamics Course
- Relationship Management in Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Sales Course
- Installation and Configuration in Microsoft Dynamics NAV Course
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016 Trade & Logistics Course
- micrMicrosoft Dynamics NAV 2016 Core Setup and Finance Courseosoft
- Exploring Microsoft Dynamics NAV Course
- Installing and Configuring Microsoft Dynamics NAV Course
- Fixed Assets in Microsoft Dynamics NAV Course
- Finance Essentials in Microsoft Dynamics NAV Course
- Finance Advanced in Microsoft Dynamics NAV Course
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV Course
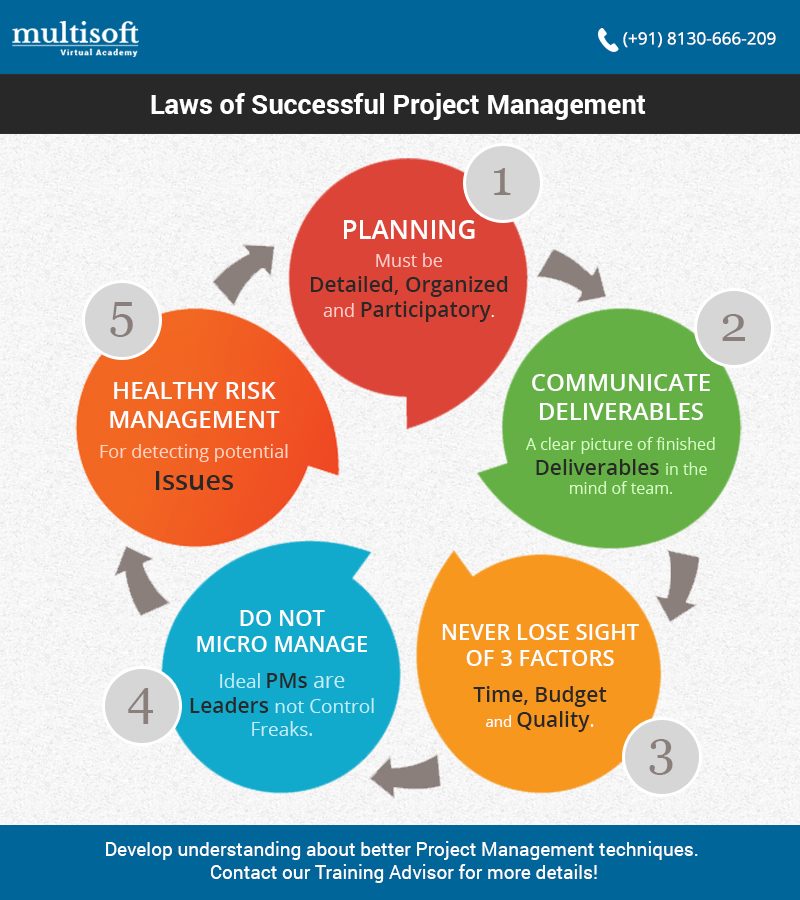



 Join our Live Instructor-Led online classes delivered by industry experts
Join our Live Instructor-Led online classes delivered by industry experts